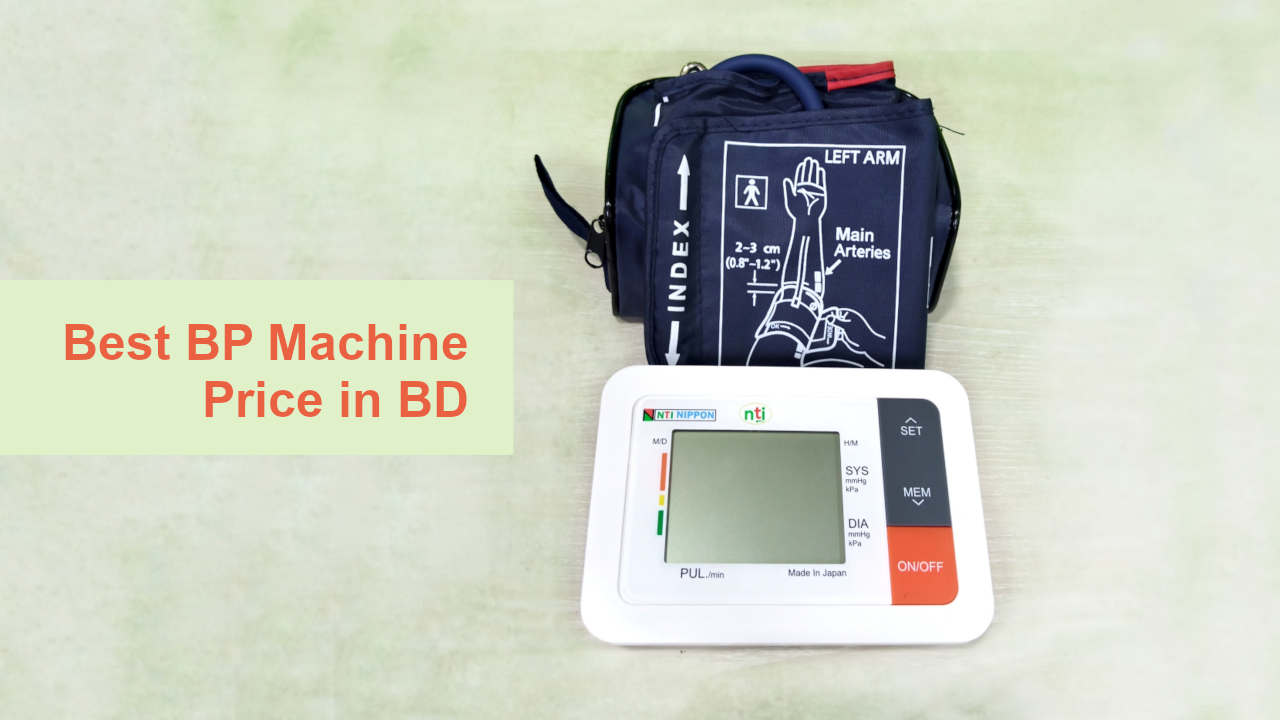
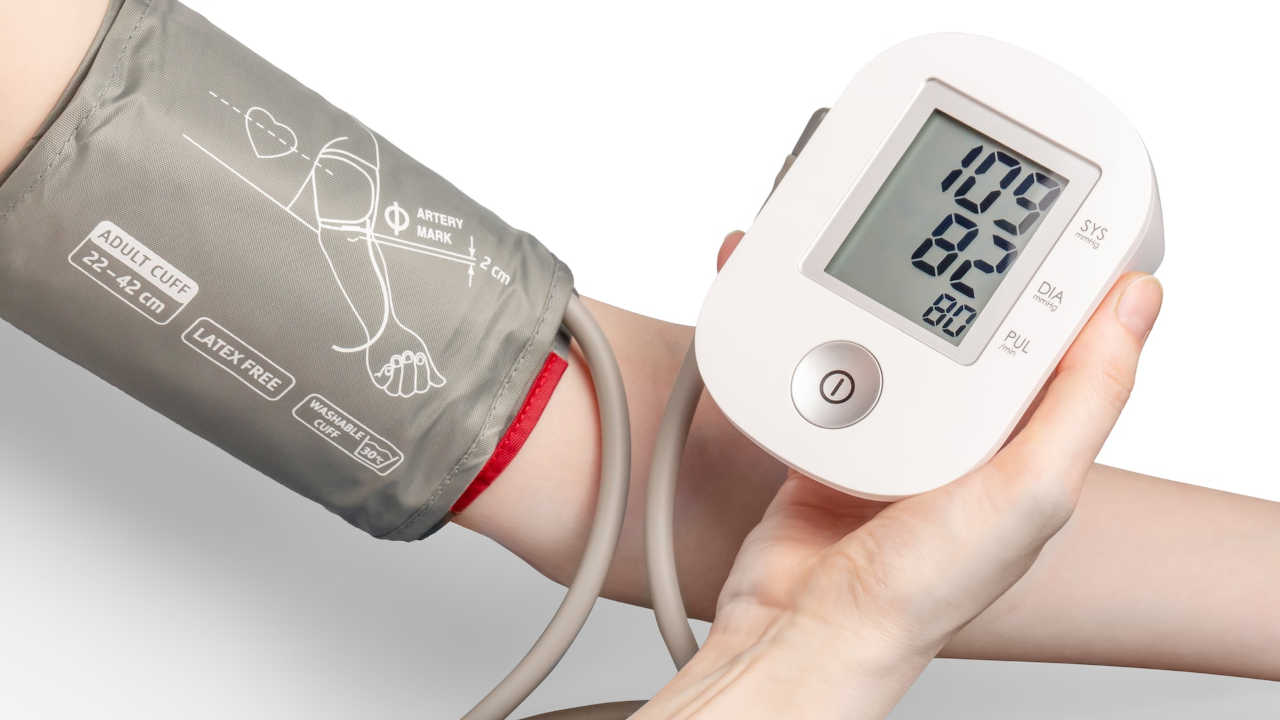
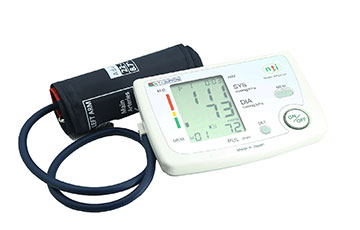
In today's digital age, the classic analog blood pressure machine still holds a special place in the hearts of medical professionals and patients alike. From their reliability and longevity to the nostalgia associated with their use, analog blood pressure machines remain an essential tool in monitoring cardiovascular health. In this blog post, we will explore some key aspects of these timeless devices and reveal why they continue to be a popular choice in healthcare settings.
Understanding Analog Blood Pressure Machines
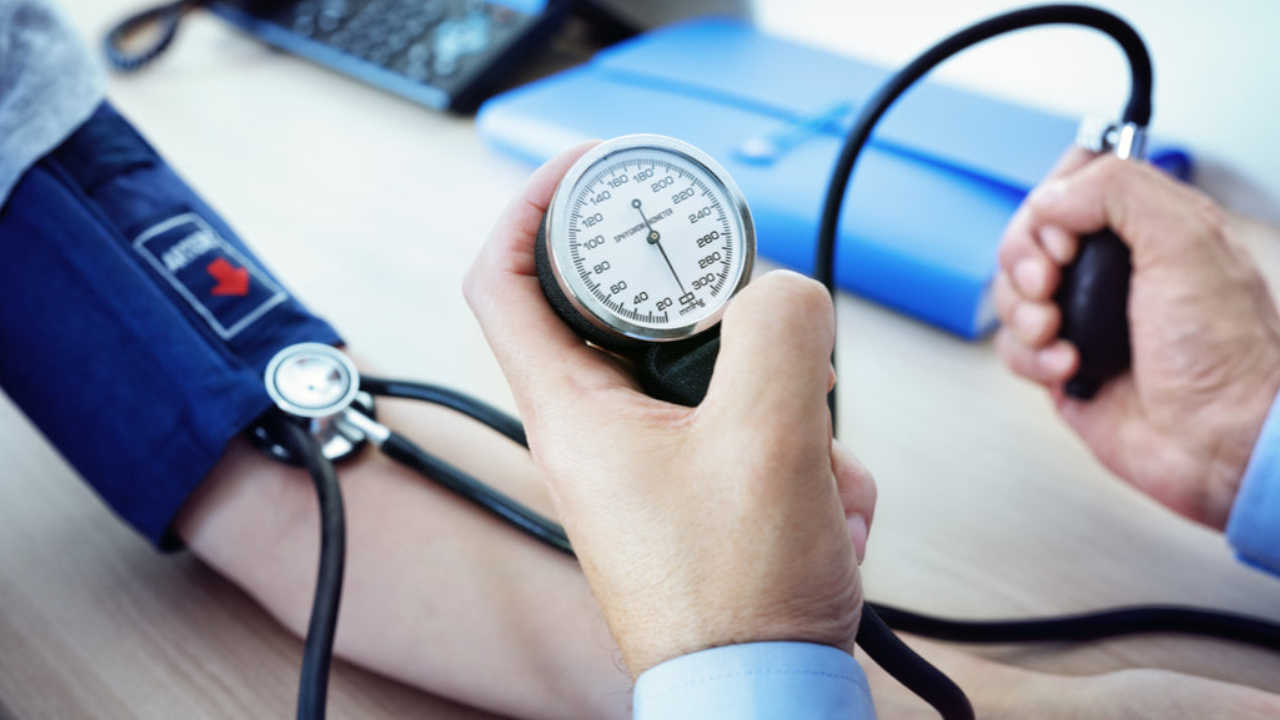
Analog blood pressure machines, also known as sphygmomanometers, consist of an inflatable cuff, a bulb to inflate the cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope. These tried-and-true devices work by manually measuring the blood pressure of an individual through the auscultation method. This involves listening for distinct sounds, called Korotkoff sounds, with a stethoscope as the cuff deflates.
Advantages of Using Analog Blood Pressure Machines
1. Accuracy: One of the primary reasons for the continued use of analog blood pressure machines is their accuracy. Digital alternatives can sometimes provide inaccurate readings due to battery-related issues or movement from the patient. In contrast, analog devices rely on meticulous manual assessment and tend to provide consistently accurate results.
2. Durability: Another advantage is their durability. Analog blood pressure machines are often built with robust materials and simplistic designs. As a result, they can withstand years of use with minimal breakdowns or malfunctions.
3. Power-independent: Since these devices do not rely on electricity or batteries, they are ideal for use in remote locations or during power outages.
4. Cost-effective: Finally, the affordability of analog blood pressure machines makes them an attractive option for many healthcare providers and facilities operating on tight budgets.
Proper Use and Maintenance Tips
To ensure the consistent performance of your analog blood pressure machine:
1. Validate its accuracy by comparing it to another calibrated device periodically.
2. Check for any visible damages or issues with the tubing, cuff, and pressure gauge.
3. Clean and disinfect the device following the manufacturer's directions and store it in a safe and dry place.
4. Ensure that the cuff fits properly on your patient's arm for precise measurement.
Conclusion
Despite advancements in digital technology, analog blood pressure machines continue to be a reliable and efficient choice for monitoring cardiovascular health. Their accuracy, durability, power independence, and cost-effectiveness make them an indispensable part of any healthcare setting. So whether you're a seasoned medical professional or simply care about keeping a close eye on your heart health, consider the merits of an analog blood pressure machine as an essential tool for your blood pressure monitoring needs.